|
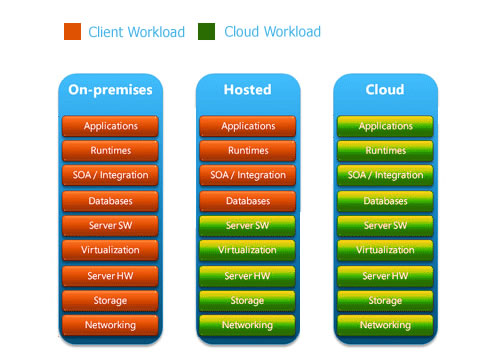
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing is a general
term for anything that involves delivering hosted
services over the Internet. These services are broadly
divided into three categories:
Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS),
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS)and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS).
The name cloud computing was inspired by the cloud
symbol that's often used to represent the Internet in
flowcharts and diagrams.
A cloud service has three
distinct characteristics that differentiate it from
traditional hosting. It is sold on demand, typically by
the minute or the hour; it is elastic -- a user can have
as much or as little of a service as they want at any
given time; and the service is fully managed by the
provider (the consumer needs nothing but a personal
computer and Internet access). Significant innovations
in virtualization and distributed computing, as well as
improved access to high-speed Internet and a weak
economy, have accelerated interest in cloud computing.
A cloud can be private or
public. A public cloud sells services to anyone on the
Internet. (Currently, Amazon Web Services is the largest
public cloud provider.) A private cloud is a proprietary
network or a data center that supplies hosted services
to a limited number of people. When a service provider
uses public cloud resources to create their private
cloud, the result is called a virtual private cloud.
Private or public, the goal of cloud computing is to
provide easy, scalable access to computing resources and
IT services.
Advantages of Cloud Computing
-
Clients would be able to access their applications
and data from anywhere at any time. They could
access the cloud computing system using any computer
linked to the Internet. Data wouldn't be confined to
a hard drive on one user's computer or even a
corporation's internal network.
-
It could bring hardware costs down. Cloud computing
systems would reduce the need for advanced hardware
on the client side. You wouldn't need to buy the
fastest computer with the most memory, because the
cloud system would take care of those needs for you.
Instead, you could buy an inexpensive computer
terminal. The terminal could include a monitor,
input devices like a keyboard and mouse and just
enough processing power to run the middleware
necessary to connect to the cloud system. You
wouldn't need a large hard drive because you'd store
all your information on a remote computer.
-
Corporations that rely on computers have to make
sure they have the right software in place to
achieve goals. Cloud computing systems give these
organizations company-wide access to computer
applications. The companies don't have to buy a set
of software or software licenses for every employee.
Instead, the company could pay a metered fee to a
cloud computing company.
-
Servers and digital storage devices take up space.
Some companies rent physical space to store servers
and databases because they don't have it available
on site. Cloud computing gives these companies the
option of storing data on someone else's hardware,
removing the need for physical space on the front
end.
-
Corporations might save money on IT support.
Streamlined hardware would, in theory, have fewer
problems than a network of heterogeneous machines
and operating systems.
-
If the cloud computing system's back end is a grid
computing system, then the client could take
advantage of the entire network's processing power.
Often, scientists and researchers work with
calculations so complex that it would take years for
individual computers to complete them. On a grid
computing system, the client could send the
calculation to the cloud for processing. The cloud
system would tap into the processing power of all
available computers on the back end, significantly
speeding up the calculation.
Disadvantages of Cloud Computing
Perhaps the biggest concerns about cloud computing are
security and privacy. The idea of handing over important
data to another company worries some people. Corporate
executives might hesitate to take advantage of a cloud
computing system because they can't keep their company's
information under lock and key.
Privacy is another matter. If a client can log in from
any location to access data and applications, it's
possible the client's privacy could be compromised.
Cloud computing companies will need to find ways to
protect client privacy. One way is to use authentication
techniques such as user names and passwords. Another is
to employ an authorization format - each user can access
only the data and applications relevant to his or her
job.
|
|
